How to debug a publish or optimization warning
This guide covers two site publishing errors—publishing and optimization errors—and their resolution strategies.
1. Publishing errors
If a publishing error occurs, you’ll see a toast notification:
“Failed to publish because there is an error on a page.”
A Review button will also be provided.
Common causes of publishing errors
Dynamic runtime errors:
The site compiler timed out while waiting for a component to build.
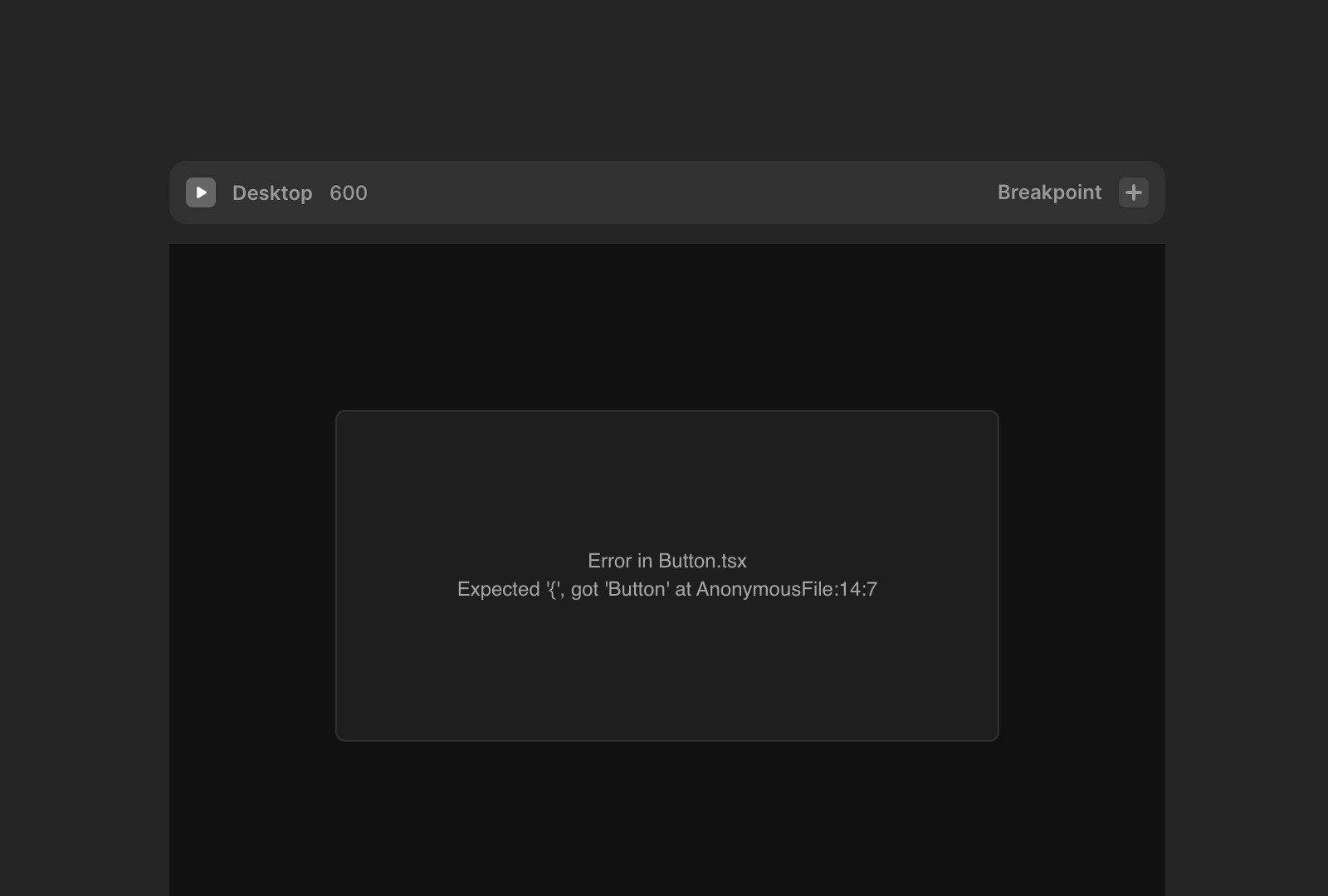
Example error in the web inspector:
ensureComponentsInLoader: Component loader not updated in time.Solution: Retry publishing. If the issue persists, fix or remove the problematic component.
Missing used components:
A component might no longer be available due to a file rename, function rename, or a loading error.
Clicking the Review button will highlight the missing component as a grey error placeholder in the layer panel.
Solution: Fix or replace the missing component.
2. Optimization errors
What is optimization?
Framer sites are built using React. Optimization “pre-renders” your site on the server, ensuring visitors see content immediately instead of a blank page while React loads in the background.
On the server, details about the visitor (like cookies, their window size or language, etc.) are not available. If a custom code component (or override) tries to access some of these things, it will fail to execute. When this happens, you’ll see an optimization warning.
Optimization warnings vs errors
You can check optimization status under Settings → Domains or Settings → Versions.
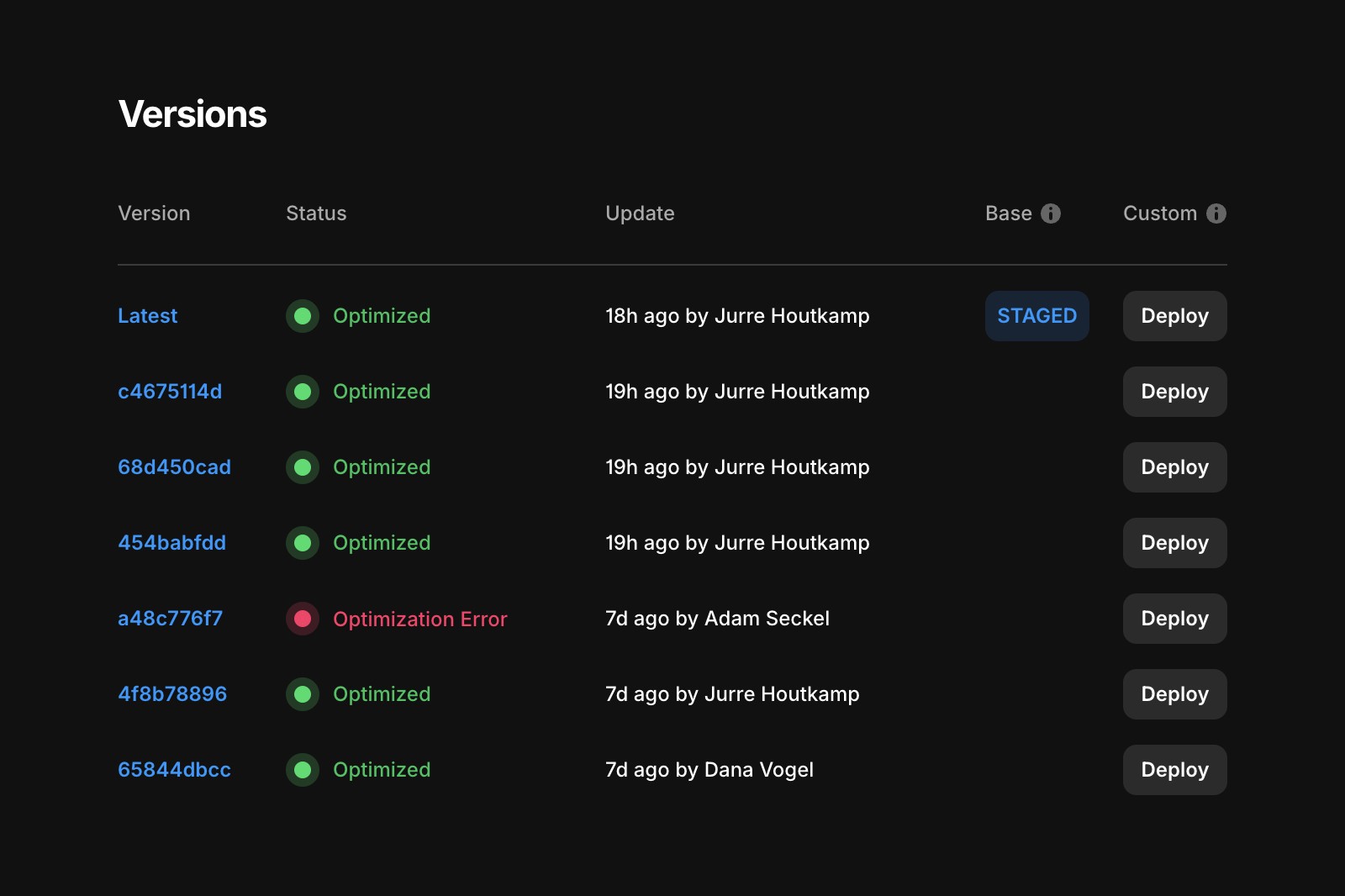
You might see one of the following statuses:
Optimized: You’re all good!
Optimization Warning: The site was successfully optimized, but something didn’t go well during optimization. (Usually, this means issues in custom code components or overrides)
Why is this bad? Your visitors might see some parts of the page missing while the page is loading (with custom code issues). Or the site’s accessibility might suffer (with nested link issues)
Optimization Error: One or more pages failed to optimize
Why is this bad? Unoptimized pages will load more slowly and have a worse SEO. In technical terms: they won’t be server-rendered, bundled, or minified, and will suffer from worse Core Web Vitals.
Common cause: custom code components or overrides
Custom code that relies on browser-specific APIs, such as window, document, or navigator, may not work properly during optimization. That’s because Framer’s server pre-renders pages without a browser environment, making these APIs unavailable.
If your code component tries to access them during server-side rendering, Framer will hide it and attempt to retry rendering when the page loads. As a result, a part of the page will be missing while the page is loading. This might be confusing to the visitor!
To fix a custom code error, follow this guide: How to fix custom code optimization errors
By addressing these warnings and utilizing Framer’s built-in tools, you can enhance site performance, improve SEO, and create a better experience for your visitors.
If you're still experiencing issues, please reach out to us through our contact page for further help.
What should I do if I encounter a publishing error in Framer?
If a publishing error occurs, you’ll see a toast notification: 'Failed to publish because there is an error on a page.' A Review button will also be provided. Common causes include dynamic runtime errors (such as the site compiler timing out while waiting for a component to build) and missing used components (due to file or function renames, or loading errors). To resolve, retry publishing. If the issue persists, fix or remove the problematic component, or replace any missing components highlighted in the layer panel.
How can I identify and fix optimization errors or warnings in Framer?
You can check your site's optimization status under Settings → Domains or Settings → Versions. If you see an Optimization Warning, it means the site was successfully optimized but there were issues, often with custom code components or overrides. An Optimization Error means one or more pages failed to optimize, which can negatively impact load speed and SEO. To fix, review any custom code that relies on browser-specific APIs (like window, document, or navigator), as these are unavailable during server-side rendering. Follow Framer’s guide on fixing custom code optimization errors for detailed steps.
Why do custom code components cause optimization issues in Framer, and how can I prevent them?
Custom code components or overrides that use browser-specific APIs such as window, document, or navigator may not work during optimization because Framer pre-renders pages on the server, where these APIs are unavailable. If your code tries to access them during server-side rendering, Framer will hide the component and retry rendering when the page loads, which can result in missing content for visitors. To prevent this, ensure your custom code does not rely on these APIs during server-side rendering, or follow Framer’s guide to fix such errors.
Updated